Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES), operated by the United States'
Image:GOES coverage.svg, Coverage map of GOES-11 and GOES-12 when active (2007).
Image:GOES12Fulldiskvisible.png, GOES-12 visible light image.
Image:GOES12Fulldiskwatervapor.png, GOES-12 water vapor image.
 Designed to operate in
Designed to operate in 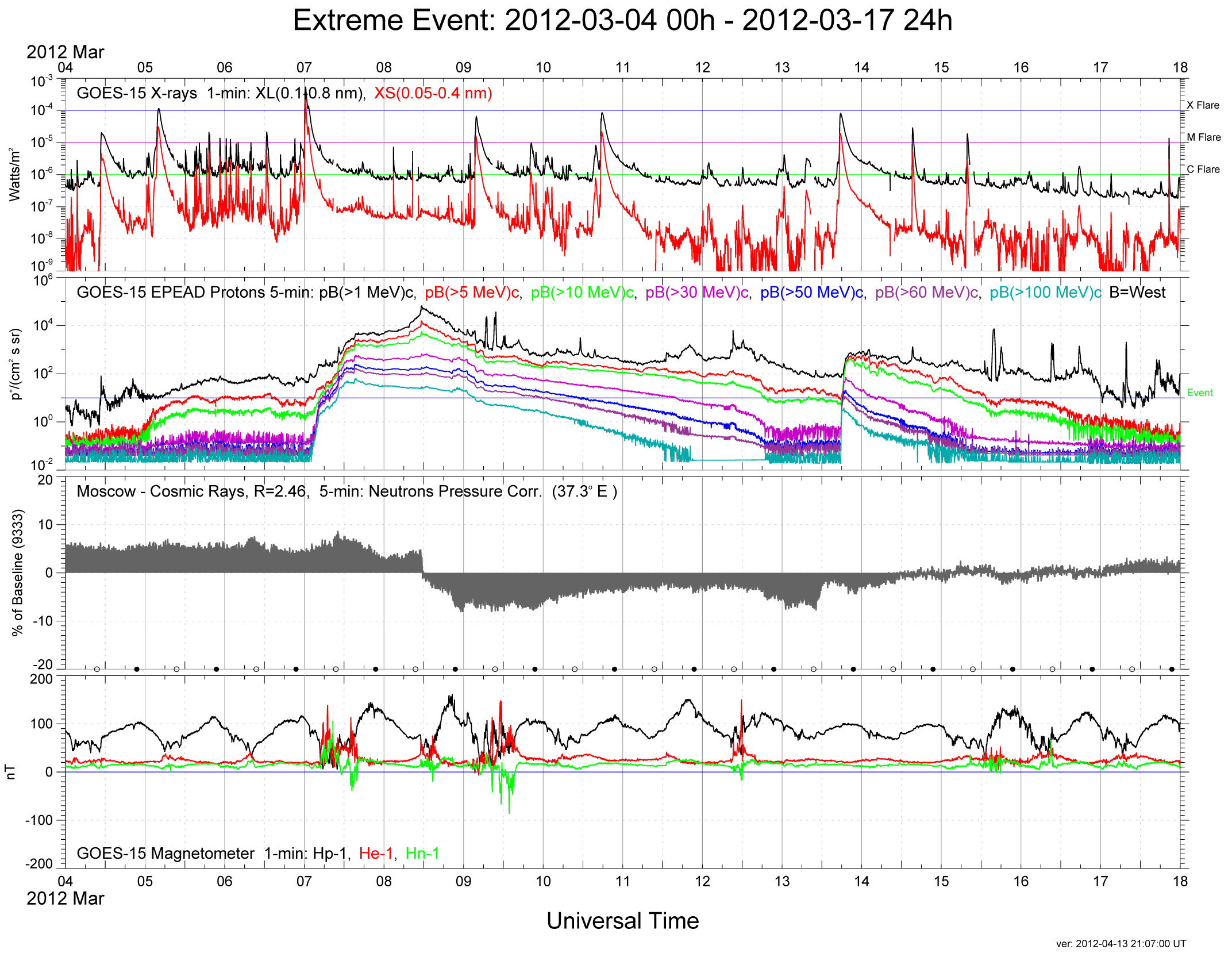 GOES-12 and above also have provided a platform for the Solar X-Ray Imager (SXI) and space environment monitoring (SEM) instruments.
The SXI provides high-cadence monitoring of large scale solar structures to support the Space Environment Services Center's (SESC) mission. The SXI unit on GOES-13, however, was damaged by a solar flare in 2006. The SESC, as the nation's "space weather" service, receives, monitors, and interprets a wide variety of solar-terrestrial data. It also issues reports, alerts, and forecasts for special events such as solar flares or geomagnetic storms. This information is important to the operation of military and civilian radio wave and satellite communication and navigation systems. The information also is important to electric power networks, the missions of geophysical explorers, Space Station astronauts, high-altitude aviators, and scientific researchers.
The SEM measures the effect of the Sun on the near-Earth solar-terrestrial electromagnetic environment, providing real-time data to the SESC.
GOES-12 and above also have provided a platform for the Solar X-Ray Imager (SXI) and space environment monitoring (SEM) instruments.
The SXI provides high-cadence monitoring of large scale solar structures to support the Space Environment Services Center's (SESC) mission. The SXI unit on GOES-13, however, was damaged by a solar flare in 2006. The SESC, as the nation's "space weather" service, receives, monitors, and interprets a wide variety of solar-terrestrial data. It also issues reports, alerts, and forecasts for special events such as solar flares or geomagnetic storms. This information is important to the operation of military and civilian radio wave and satellite communication and navigation systems. The information also is important to electric power networks, the missions of geophysical explorers, Space Station astronauts, high-altitude aviators, and scientific researchers.
The SEM measures the effect of the Sun on the near-Earth solar-terrestrial electromagnetic environment, providing real-time data to the SESC.
"GOES I–M Databook"
and th
respectively. The GOES-R series is being built by
National Weather Service Satellite Images (current plus 3,6,12 and 24 hr loops)
LM/SAIC/IBM partnership announced for GOES
GOES gallery
Spherical panorama of GOES-O in the clean room
GOES terrestrial data
{{authority control *
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
(NOAA)'s National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service
The National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service (NESDIS) was created by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to operate and manage the United States environmental satellite programs, and manage the data g ...
division, supports weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology forecasting, to predict the conditions of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia a ...
, severe storm tracking, and meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not ...
research. Spacecraft and ground-based elements of the system work together to provide a continuous stream of environmental data. The National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an Government agency, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weathe ...
(NWS) and the Meteorological Service of Canada
The Meteorological Service of Canada (MSC; french: Service météorologique du Canada – SMC) is a division of Environment and Climate Change Canada, which primarily provides public meteorological information and weather forecasts and warnings ...
use the GOES system for their North American weather monitoring and forecasting operations, and scientific researchers use the data to better understand land, atmosphere, ocean, and climate dynamics.
The GOES system uses geosynchronous equatorial satellite
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude ...
s that, since the launch of SMS-1
The Synchronous Meteorological Satellite (SMS) program, was a program where NASA developed two weather satellites; which were placed into geosynchronous orbit.
History
SMS-1 was launched May 17, 1974 and SMS-2 was launched February 6, 1975. B ...
in 1974, have been a basic element of U.S. weather monitoring and forecasting.
The procurement, design, and manufacture of GOES satellites is overseen by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
.
NOAA is the official provider of both GOES terrestrial data and GOES space weather data. Data can also be accessed using the SPEDAS
SPEDAS (Space Physics Environment Data Analysis System) is an open-source data analysis tool intended for Space Physics users. It was developed using Interactive Data Language (IDL).
Overview
SPEDAS is free software that can download and man ...
software.
History
The first GOES satellite, GOES-1, was launched in October 1975. Two more followed, launching almost two minutes short of a year apart, on 16 June 1977 and 1978 respectively. Prior to the GOES satellites twoSynchronous Meteorological Satellite
The Synchronous Meteorological Satellite (SMS) program, was a program where NASA developed two weather satellites; which were placed into geosynchronous orbit.
History
SMS-1 was launched May 17, 1974 and SMS-2 was launched February 6, 1975. Bot ...
s (SMS) satellites had been launched; SMS-1
The Synchronous Meteorological Satellite (SMS) program, was a program where NASA developed two weather satellites; which were placed into geosynchronous orbit.
History
SMS-1 was launched May 17, 1974 and SMS-2 was launched February 6, 1975. B ...
in May 1974, and SMS-2
The Synchronous Meteorological Satellite (SMS) program, was a program where NASA developed two weather satellites; which were placed into geosynchronous orbit.
History
SMS-1 was launched May 17, 1974 and SMS-2 was launched February 6, 1975. Bo ...
in February 1975. The SMS-derived satellites were spin-stabilized spacecraft, which provided imagery through a Visible and Infrared Spin Scan Radiometer
Visibility, in meteorology, is a measure of the distance at which an object or light can be seen.
Visibility may also refer to:
* A measure of turbidity in water quality control
* Interferometric visibility, which quantifies interference contrast ...
, or VISSR. The first three GOES satellites used a Philco-Ford
Philco (an acronym for Philadelphia Battery Company) is an American electronics manufacturer headquartered in Philadelphia. Philco was a pioneer in battery, radio, and television production. In 1961, the company was purchased by Ford and, from 196 ...
bus developed for the earlier Synchronous Meteorological Satellite
The Synchronous Meteorological Satellite (SMS) program, was a program where NASA developed two weather satellites; which were placed into geosynchronous orbit.
History
SMS-1 was launched May 17, 1974 and SMS-2 was launched February 6, 1975. Bot ...
s (SMS) generation.
Following the three SMS GOES spacecraft, five satellites were procured from Hughes
Hughes may refer to:
People
* Hughes (surname)
* Hughes (given name)
Places Antarctica
* Hughes Range (Antarctica), Ross Dependency
* Mount Hughes, Oates Land
* Hughes Basin, Oates Land
* Hughes Bay, Graham Land
* Hughes Bluff, Victoria La ...
, which became the first generation GOES satellites. Four of these reached orbit, with GOES-G
GOES-G was a weather satellite to be operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite was designed to sense and monitor meteorological conditions from a geostationary orbit, intended to replace GOES-5 and provide c ...
being lost in a launch failure.
The next five GOES satellites were constructed by Space Systems/Loral
SSL, formerly Space Systems/Loral, LLC (SS/L), of Palo Alto, California, is a wholly owned manufacturing subsidiary of Maxar Technologies.
SSL designs and builds satellites and space systems for a wide variety of government and commercial cust ...
, under contract to NASA. The imager and sounder instruments were produced by ITT Aerospace/Communication Division. GOES-8 and -9 were designed to operate for three years, while -10, -11 and -12 have expected lifespans of five years. GOES-11 and -12 were launched carrying enough fuel for ten years of operation, in the event that they survived beyond their expected lifespan.
A contract to develop four third-generation GOES satellites was awarded to Hughes Corporation, with the satellites scheduled for launch on Delta III
Delta III was an expendable launch vehicle made by Boeing. The vehicle was developed from the highly-successful Delta II to help meet the launch demand of larger satellites. The first Delta III launch was on August 26, 1998. Of its three flights ...
rockets between 2002 and 2010. After a merger with Hughes, Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product ...
took over the development contracts, with launches transferred to the Delta IV
Delta IV is a group of five expendable launch systems in the Delta (rocket family), Delta rocket family introduced in the early 2000s. Originally designed by Boeing's Defense, Space and Security division for the National Security Space Launch, ...
, following the Delta III's retirement. The contract for the fourth satellite, GOES-Q, was later cancelled, and that satellite will only be completed in the event that another third-generation satellite is lost in a launch failure or fails soon after launch. The first third-generation satellite, GOES-13, was launched in May 2006, originally serving as an on-orbit backup. However, in April 2010, GOES-12 was moved to South America coverage and GOES-13 was moved to the GOES-East role. Third generation satellites have an expected lifespan of seven years, but will carry excess fuel to allow them to operate for longer if possible, as with the last two-second generation satellites.
The fourth-generation satellites, the GOES-R series, are being built by Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
using the A2100 satellite bus. The GOES-R series is a four-satellite program (GOES-R, -S, -T and -U) that will extend the availability of the operational GOES satellite system through 2036. The first satellite of the series, the eponymous GOES-R, was launched on 19 November 2016. It was renamed GOES-16
GOES-16, formerly known as GOES-R before reaching geostationary orbit, is the first of the GOES-R series of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) operated by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration&n ...
upon reaching orbit. The second satellite of the series, GOES-S, was launched on 1 March 2018. It was renamed GOES-17
GOES-17 (designated pre-launch as GOES-S) is an environmental satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The satellite is second in the four-satellite GOES-R series (GOES-16, -17, - T, and - U). GOES-17 su ...
upon reaching orbit.
Satellites
Operationally available
Four GOES satellites are available for operational use. GOES-14 is in storage at 105° W. The launch of this satellite, which was designated GOES-O before orbiting, was delayed several times. It was launched successfully on 27 June 2009 from Space Launch Complex 37, piggybacking on a Delta IV rocket. It underwent Post-Launch Testing until December 2009 and then was placed in on-orbit storage. This satellite is a part of the GOES-N Series. GOES-14 has been and will be activated should another GOES satellite suffer a problem or be decommissioned. It was temporarily designated GOES-East because of technical difficulties with GOES-13 and moved towards the GOES-East location. After resolution of those problems, GOES-14 was returned to storage.GOES-15
GOES-15, previously known as GOES-P, is an American weather satellite, which forms part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) system operated by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The spacecraft was ...
, which was designated GOES-P before orbiting, was launched successfully on 4 March 2010. From 2011 to 2018, it occupied the GOES-West position at 135°W over the Pacific Ocean. It moved eastward to 128° W beginning on 29 October 2018 in order to make room for GOES-17
GOES-17 (designated pre-launch as GOES-S) is an environmental satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The satellite is second in the four-satellite GOES-R series (GOES-16, -17, - T, and - U). GOES-17 su ...
, which took over the GOES-West position on 10 December 2018. It is currently operating in parallel with GOES-17 for user evaluation purposes, but it is scheduled to be retired sometime after 2019.
GOES-16
GOES-16, formerly known as GOES-R before reaching geostationary orbit, is the first of the GOES-R series of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) operated by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration&n ...
occupies the GOES-East position at 75° W. This satellite, which was designated GOES-R before orbiting, was launched by an Atlas V rocket
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Martin ...
from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the statio ...
in Florida on 19 November 2016. It underwent Post-Launch Testing through early 2017 before replacing GOES-13 as GOES-East.
GOES-17
GOES-17 (designated pre-launch as GOES-S) is an environmental satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The satellite is second in the four-satellite GOES-R series (GOES-16, -17, - T, and - U). GOES-17 su ...
occupies the GOES-West position at 137.2° W. The satellite, designated as GOES-S before orbiting, was launched by an Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on 1 March 2018. Following post-launch testing and troubleshooting of a problem in its imager, the satellite was declared operational in February 2019.
Inactive or repurposed
Several GOES satellites are still in orbit but are either inactive or have been re-purposed. AlthoughGOES-3
GOES-3, known as GOES-C before becoming operational, was an American geostationary weather and communications satellite. It was originally built for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as part of the Geostationary Operational En ...
ceased to be used for weather operations in 1989, it spent over 20 years as a critical part of communications between the U.S. and Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station
The Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station is the United States scientific research station at the South Pole of the Earth. It is the southernmost point under the jurisdiction (not sovereignty) of the United States. The station is located on the ...
before being decommissioned in 2016. Geostationary satellites expend fuel to keep themselves stationary over the equator, and thus cannot normally ordinarily be seen from the poles. When that fuel is depleted, solar and lunar perturbations increase the satellite's inclination so that its ground track
A ground track or ground trace is the path on the surface of a planet directly below an aircraft's or satellite's trajectory. In the case of satellites, it is also known as a suborbital track, and is the vertical projection of the satellite's or ...
begins to describe an analemma
In astronomy, an analemma (; ) is a diagram showing the position of the Sun in the sky as seen from a fixed location on Earth at the same mean solar time, as that position varies over the course of a year. The diagram will resemble a figure ei ...
(a figure-8 in the north-south direction). This usually ends the satellite's primary mission. However, when the inclination is high enough the satellite may begin to rise above the polar horizons at the extremes of the figure-8, as was the case for GOES-3. A nine-meter dish was constructed at the station, and communication with the satellite could be obtained for about five hours per day. Data rates were around 2.048 megabytes/second (bi-directional) under optimum conditions.
GOES-8, which was designated GOES-I before orbiting, was the GOES-East satellite when it was in operation. It is in a parking orbit and is drifting westerly at a rate of about 4° daily. It was decommissioned on 1 April 2003 and deactivated on 5 May 2004 after the failure of its propulsion system.
GOES-10, which was designated GOES-K before orbiting, was decommissioned on 2 December 2009 and was boosted to a graveyard orbit
A graveyard orbit, also called a junk orbit or disposal orbit, is an orbit that lies away from common operational orbits. One significant graveyard orbit is a supersynchronous orbit well beyond geosynchronous orbit. Some satellites are moved int ...
. It no longer had the fuel for required maneuvers to keep it on station.
GOES-11, which was designated GOES-L before orbiting, had a partial failure on 6 December 2011. It was decommissioned on 16 December 2011 and boosted into a graveyard orbit.
GOES-12
GOES-12, known as GOES-M before becoming operational, is an American weather satellite, which is part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. It was launched on July 23, ...
, which was designated GOES-M before orbiting, was decommissioned on 16 August 2013 and boosted into a graveyard orbit.
GOES-13, which was designated GOES-N before orbiting, was decommissioned on 3 January 2018 and boosted into storage orbit. It is transferred to the U.S. Space Force
The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space service branch of the U.S. Armed Forces, one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and the world's only independent space force. Along with its sister branch, the U.S. Air Force, the Space ...
and positioned at 61.5ºE under the new name EWS-G1.
Purpose
 Designed to operate in
Designed to operate in geostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitud ...
above the Earth, the GOES spacecraft continuously view the continental United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
, the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southe ...
, and southern Canada. The three-axis, body-stabilized design enables the sensors to "stare" at the Earth and thus more frequently image clouds, monitor the Earth's surface temperature and water vapour
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
fields, and sound the atmosphere for its vertical thermal and vapor structures. The evolution of atmospheric phenomena can be followed, ensuring real-time coverage of meteorological events such as severe local storms and tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s. The importance of this capability was proven during hurricanes Hugo
Hugo or HUGO may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Hugo'' (film), a 2011 film directed by Martin Scorsese
* Hugo Award, a science fiction and fantasy award named after Hugo Gernsback
* Hugo (franchise), a children's media franchise based on ...
(1989) and Andrew
Andrew is the English form of a given name common in many countries. In the 1990s, it was among the top ten most popular names given to boys in List of countries where English is an official language, English-speaking countries. "Andrew" is freq ...
(1992).
The GOES spacecraft also enhance operational services and improve support for atmospheric science research, numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in th ...
models, and environmental sensor design and development.
Satellite data is broadcast on the L-band
The L band is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) designation for the range of frequencies in the radio spectrum from 1 to 2 gigahertz (GHz). This is at the top end of the ultra high frequency (UHF) band, at the lower en ...
, and received at the NOAA Command and Data Acquisition ground station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves fro ...
at Wallops Island, Virginia from which it is disseminated to users. Additionally, anyone may receive data directly from the satellites by utilizing a small dish, and processing the data with special software.
The GOES satellites are controlled from the Satellite Operations Control Center in Suitland, Maryland. During significant weather or other events, the normal schedules can be altered to provide the coverage requested by the NWS and other agencies.
 GOES-12 and above also have provided a platform for the Solar X-Ray Imager (SXI) and space environment monitoring (SEM) instruments.
The SXI provides high-cadence monitoring of large scale solar structures to support the Space Environment Services Center's (SESC) mission. The SXI unit on GOES-13, however, was damaged by a solar flare in 2006. The SESC, as the nation's "space weather" service, receives, monitors, and interprets a wide variety of solar-terrestrial data. It also issues reports, alerts, and forecasts for special events such as solar flares or geomagnetic storms. This information is important to the operation of military and civilian radio wave and satellite communication and navigation systems. The information also is important to electric power networks, the missions of geophysical explorers, Space Station astronauts, high-altitude aviators, and scientific researchers.
The SEM measures the effect of the Sun on the near-Earth solar-terrestrial electromagnetic environment, providing real-time data to the SESC.
GOES-12 and above also have provided a platform for the Solar X-Ray Imager (SXI) and space environment monitoring (SEM) instruments.
The SXI provides high-cadence monitoring of large scale solar structures to support the Space Environment Services Center's (SESC) mission. The SXI unit on GOES-13, however, was damaged by a solar flare in 2006. The SESC, as the nation's "space weather" service, receives, monitors, and interprets a wide variety of solar-terrestrial data. It also issues reports, alerts, and forecasts for special events such as solar flares or geomagnetic storms. This information is important to the operation of military and civilian radio wave and satellite communication and navigation systems. The information also is important to electric power networks, the missions of geophysical explorers, Space Station astronauts, high-altitude aviators, and scientific researchers.
The SEM measures the effect of the Sun on the near-Earth solar-terrestrial electromagnetic environment, providing real-time data to the SESC.
Payload
The main mission of a GOES satellite is carried out by the primary payload instruments, which are the Imager and the Sounder. The Imager is a multichannel instrument that senses infraredradiant energy
Radiant may refer to:
Computers, software, and video games
* Radiant (software), a content management system
* GtkRadiant, a level editor created by id Software for their games
* Radiant AI, a technology developed by Bethesda Softworks for '' ...
and visible reflected solar energy from the Earth's surface and atmosphere. The Sounder provides data for vertical atmospheric temperature and moisture profiles, surface and cloud top temperature, and ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
distribution.
GOES also offers the ''Data Collection System'', a ground-based meteorological platform satellite data collection
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. C ...
and relay service.
Other instruments on board the spacecraft are the SEM set, which consists of a magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, o ...
, an X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
sensor, a high energy proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
and alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produce ...
detector, and an energetic particles sensor.
The GOES-N series (GOES-13 through GOES-15) spacecraft also have a sun-pointed extreme ultraviolet sensor.
In addition, the GOES satellites carry a search and rescue repeater that collects data from Emergency Position-Indicating Radio Beacon
An Emergency Position-Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB) is a type of emergency locator beacon for commercial and recreational boats, a portable, battery-powered radio transmitter used in emergencies to locate boaters in distress and in need of i ...
s and Emergency Locator Transmitter beacons, which are used during search-and-rescue operations by the U.S. Air Force Rescue Coordination Center {{Use dmy dates, date=January 2021
As the United States' inland search and rescue (SAR) coordinator, the Air Force Rescue Coordination Center (AFRCC) serves as the single agency responsible for coordinating on-land federal SAR activities in the Unit ...
.
GOES-R Series
The proposed instrument package for the GOES-R series initially included the following: * Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) * Hyperspectral Environmental Suite (HES) * Space Environment In-Situ Suite (SEISS), which includes two Magnetospheric Particle Sensors (MPS-HI and MPS-LO), an Energetic Heavy Ion Sensor, and a Solar and Galactic Proton Sensor * Solar Imaging Suite, which includes the Solar Ultraviolet Imager (SUVI), the Solar X-Ray Sensor (XRS), and the Extreme Ultraviolet Sensor (EUVS) *Geostationary Lightning Mapper
GOES-16, formerly known as GOES-R before reaching geostationary orbit, is the first of the GOES-R series of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) operated by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration&n ...
(GLM)
* Magnetometer
In September 2006, the HES was canceled.
Satellite designations
Before being launched, GOES satellites are designated by letters (A, B, C, etc.). Once a GOES satellite is launched successfully, it is redesignated with a number (1, 2, 3, etc.). So, GOES-A to GOES-F became GOES-1 to GOES-6. BecauseGOES-G
GOES-G was a weather satellite to be operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite was designed to sense and monitor meteorological conditions from a geostationary orbit, intended to replace GOES-5 and provide c ...
was a launch failure, it never received a number. GOES-H to GOES-R became GOES-7 to GOES-16 (skipping GOES-Q, which was not built).
Once operational, the different locations used by the satellites are given a name corresponding to the regions they cover. These are GOES-East and GOES-West, which watch the eastern and western halves of the U.S., respectively. GOES-East is occupied by GOES-16, while GOES-West is occupied by GOES-17. The -East/-West designation is used more frequently than the satellite's number designation. GOES-IO (Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
), a new designation revealed in early May 2020, is currently occupied by GOES-13 (DOD-1).
There was also a GOES-South position, which is meant to provide dedicated coverage of South America. Before the GOES-R series became operational, unless a satellite was dedicated to this continent, imagery of South America was updated every 3 hours instead of every 30 minutes. The GOES-South station was usually assigned to older satellites whose North American operations have been taken over by new satellites. For example, GOES-10 was moved from the GOES-West position to GOES-South after it was replaced in the -West station by GOES-11. When GOES-10 was decommissioned on 1 December 2009, GOES-South was taken over by GOES-12. Since the retirement of GOES-12 on 16 August 2013, the GOES-South station has been unoccupied. GOES-16 has since made the need for a dedicated GOES-South satellite obsolete; as of 2019, the satellite produces full disk images every 10 minutes.
Development of GOES-R Series
In September 2006, NOAA reduced the planned number of GOES-R satellites from four to two because of cost overrun concerns. The planned delivery schedule was also slowed down to reduce costs. The expected cost of the series is $7.69 billion, a $670 million increase from the prior $7 billion estimate. The contract for constructing the satellites and manufacturing the magnetometer, SUVI, and GLM was awarded to Lockheed Martin. This award was challenged by losing bidder Boeing; however, the protest was subsequently dismissed. The ABI instrument was delivered byL3Harris
L3Harris Technologies (L3Harris) is an American technology company, defense contractor, and information technology services provider that produces C6ISR systems and products, wireless equipment, tactical radios, avionics and electronic systems, ...
(formerly ITT Exelis
ITT may refer to:
Communication
* Infantry-Tank Telephone, a device allowing infantrymen to speak to the occupants of armoured vehicles.
Mathematics
*Intuitionistic type theory, other name of Martin-Löf Type Theory
* Intensional type theory
...
). The SEISS was delivered by Assurance Technology Corporation.
XRS and EUVS are being combined into the Extreme Ultra Violet and X-Ray Irradiance Sensors (EXIS), which was delivered by the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics
The Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) is a research organization at the University of Colorado Boulder. LASP is a research institute with over one hundred research scientists ranging in fields from solar influences, to Earth' ...
of the University of Colorado
The University of Colorado (CU) is a system of public universities in Colorado. It consists of four institutions: University of Colorado Boulder, University of Colorado Colorado Springs, University of Colorado Denver, and the University of Co ...
.
The contract for the ground system, including data processing, was awarded to a team led by the Weather Systems division of L3Harris
L3Harris Technologies (L3Harris) is an American technology company, defense contractor, and information technology services provider that produces C6ISR systems and products, wireless equipment, tactical radios, avionics and electronic systems, ...
, including subcontracts to Boeing, Atmospheric and Environmental Research (AER), Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building technologies, performance ma ...
, Carr Astronautics, Wyle Laboratories
Wyle Laboratories (Wyle) is an American privately held provider of engineering, scientific and technical services to the Department of Defense, NASA, and a variety of commercial customers primarily in the aerospace industry. The company offers s ...
, and Ares
Ares (; grc, Ἄρης, ''Árēs'' ) is the Greek god of war and courage. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. The Greeks were ambivalent towards him. He embodies the physical valor necessary for success in war b ...
.
Status of GOES satellites
GOES spacecraft have been manufactured byBoeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product ...
(GOES-D through -H and GOES-N through -P) and Space Systems/Loral
SSL, formerly Space Systems/Loral, LLC (SS/L), of Palo Alto, California, is a wholly owned manufacturing subsidiary of Maxar Technologies.
SSL designs and builds satellites and space systems for a wide variety of government and commercial cust ...
(GOES-A through -C and GOES-I through -M). The GOES-I series (I-M) and the GOES-N series (N-P) are documented in th"GOES I–M Databook"
and th
respectively. The GOES-R series is being built by
Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
with the first and second in the series, GOES-16 and -17, operational .
Boeing would have built and launched GOES-Q only if GOES-O or GOES-P had failed to be delivered on-orbit in good working order.
* GOES-1, launched on 16 October 1975, ''decommissioned on 7 March 1985''
* GOES-2
GOES-2, known as GOES-B before becoming operational, was a geostationary weather satellite which was operated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite sys ...
, launched on 16 June 1977, ''decommissioned on 5 May 2001, before which a comsat for the South Pole, Peacesat''
* GOES-3
GOES-3, known as GOES-C before becoming operational, was an American geostationary weather and communications satellite. It was originally built for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as part of the Geostationary Operational En ...
, launched on 16 June 1978, ''decommissioned on 29 June 2016, before which a comsat for the South Pole, Peacesat''
* GOES-4, launched on 9 September 1980, ''decommissioned on 9 October 1988''
* GOES-5, launched on 22 May 1981, ''decommissioned 18 July 1990''
* GOES-6, launched on 28 April 1983, ''decommissioned on 19 May 1992''
* GOES-G
GOES-G was a weather satellite to be operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite was designed to sense and monitor meteorological conditions from a geostationary orbit, intended to replace GOES-5 and provide c ...
, launched on 3 May 1986, ''failed to achieve orbit''
* GOES-7, launched on 26 February 1987, ''decommissioned on 12 April 2012, before which a comsat for Peacesat''
* GOES-8, launched on 13 April 1994, ''decommissioned on 5 May 2004''
* GOES-9, launched on 23 May 1995, ''decommissioned on 15 June 2007''
* GOES-10, launched on 25 April 1997, ''decommissioned on 2 December 2009''
* GOES-11, launched on 3 May 2000, ''decommissioned on 16 December 2011''
* GOES-12
GOES-12, known as GOES-M before becoming operational, is an American weather satellite, which is part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. It was launched on July 23, ...
, launched on 23 July 2001, ''decommissioned on 16 August 2013, before which provided coverage for South America''
* GOES-13, launched on 24 May 2006, ''decommissioned on 3 January 2018, operational again for the Indian Ocean since 8 September 2020 as EWS-G1''
* GOES-14, launched on 27 June 2009, ''in standby, located at 105° W''
* GOES-15
GOES-15, previously known as GOES-P, is an American weather satellite, which forms part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) system operated by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The spacecraft was ...
, launched on 4 March 2010, ''in operation since 14 December 2011, parallel to GOES-17 since 11 November 2018''
* GOES-16
GOES-16, formerly known as GOES-R before reaching geostationary orbit, is the first of the GOES-R series of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) operated by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration&n ...
, launched on 19 November 2016, ''in operation as GOES-East since 18 December 2017''
* GOES-17
GOES-17 (designated pre-launch as GOES-S) is an environmental satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The satellite is second in the four-satellite GOES-R series (GOES-16, -17, - T, and - U). GOES-17 su ...
, launched on 1 March 2018, ''in operation as GOES-West since 12 February 2019''
* GOES-18
GOES-18 (designated pre-launch as GOES-T) is the third of the "GOES-R Series", the current generation of weather satellites operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The current and next satellites of the Series (G ...
, launched on 1 March 2022
* GOES-U
GOES-U is a planned weather satellite, the fourth and last of the GOES-R series of satellites operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The GOES-R series will extend the availability of the Geostationary Operationa ...
, scheduled for launch in April 2024
See also
* Geostationary Extended Observations (GeoXO) * Applications Technology Satellites *Multi-Functional Transport Satellite
Multifunctional Transport Satellites (MTSAT) were a series of weather and aviation control satellites. They are replaced by Himawari 8 on 7 July 2015. They were geostationary satellites owned and operated by the Japanese Ministry of Land, Inf ...
* Polar Operational Environmental Satellites
The Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite (POES) was a constellation of polar orbiting weather satellites funded by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Mete ...
* Remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth ...
* Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera
Further reading
References
External links
National Weather Service Satellite Images (current plus 3,6,12 and 24 hr loops)
LM/SAIC/IBM partnership announced for GOES
GOES gallery
Spherical panorama of GOES-O in the clean room
GOES terrestrial data
{{authority control *